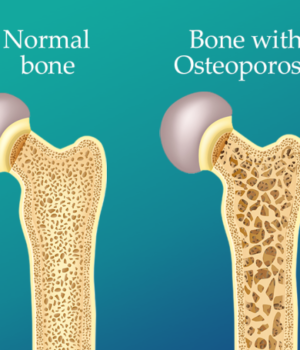
Brittle and fragile bones can result from osteoporosis, a condition that can affect both men and women. According to the National Health Service, women are at a higher risk than men, owing to the impact of hormonal changes during menopause on bone density. Decreased estrogen levels during this phase are linked to reduced bone density. Beyond this, specific medical conditions can also heighten the risk of osteoporosis. On World Osteoporosis Day, which occurs on October 20, we delve into the relationship between these medical conditions and osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, explained by Dr. Sunilkumar Singh, a consultant rheumatology surgeon at Mumbai’s Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital. Bones become so brittle that they are more prone to fractures, particularly in the spine, hip, and wrist. While natural bone density loss occurs with age, osteoporosis accelerates this process.
Certain medical conditions increase the likelihood of osteoporosis. These include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder primarily affecting the joints. Chronic inflammation associated with this condition can lead to bone loss, thereby increasing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Hyperthyroidism, a condition resulting from excessive thyroid hormone production, which accelerates bone loss and makes bones weaker and more susceptible to fractures.
- Celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten consumption, which can impair the absorption of vital nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D necessary for bone health.
- Chronic kidney disease, which can disturb the balance of calcium and phosphate in the body, consequently affecting bone density.